√ ƒŒƒCƒ„[ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒ{ƒu 50 ‘ã 721940
Activity U and F follow Activities W and D2 , and precede Activities E and R1 Activity Y follows Activities C and R , and followed by Activity L Activities D , M , and B start the project Activity C can start when Activities D , E1 and S are completed Activity RContribution Margin $38,610 $990 F $37,6 $380 U $38,000 Fixed Expenses 33,000 4,500 F 37,500 0 37,500 Operating Income/(loss) $5,610 $5,490 F $1 $380 U $500' ( ) ) ( ) ( * , / 0 1 2 3 4 / 5 3 6 7 8 6 9 1 ;

Constructing Perpendicular Lines Construction Of Geometric Figures Siyavula
ƒŒƒCƒ„[ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒ{ƒu 50 'ã
ƒŒƒCƒ„[ƒ{ƒu ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒ{ƒu 50 'ã-(b) What is the probability that a US user who downloads music, selected at random, obtained it from either the United States or Canada?X(a;b)(x a) f y(a;b)(y b) = 1 2(x 1) 2(y 1) (e) We can always use the theorem rf(a;b) ~uto compute the directional derivative at (a;b) in the direction of ~u SOLUTION False This formula only works if fis di erentiable at (a;b) (See Exercise 3 below) (f) Di erent parameterizations of the same curve result in identical tangent vectors at a




Gene Expression In Osteoblasts And Osteoclasts Under Microgravity Conditions A Systematic Review Bentham Science
Annual M anagem ent F ee M ax 1 50% per annum R epurc has e C harge N / A Perf orm anc e F ee N / A M inim um I nv es t m ent / A l l f i g u re s a re s u b j e c t t o f re q u e n t c h a n g e s o n a d a i l y b a s i s a n d t h e p e rc e n t a g e s m i g h t n o t a d d u p t o 1 0 0 % d u e t o ro u n d i n gBegin privacyenhanced message proctype 01,micclear originatorname webmaster@wwwsecgov originatorkeyasymmetricConversely, if F and Gare of class C2, then udefined by u(x,t) = F(x ct) G(x−ct) is a classical solution of (61) T The families of lines x−ct= constant and xct= constant, 42 on (x,t) plane are called the characteristics of the wave equation These are straight lines with slopes ±1/c The function G(x− ct) represents a
Word square A word square is a special type of acrostic It consists of a set of words written out in a square grid, such that the same words can be read both horizontally and vertically The number of words, which is equal to the number of letters in each word, is known as the "order" of the square551 Use substitution to evaluate indefinite integrals 552 Use substitution to evaluate definite integrals The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus gave us a method to evaluate integrals without using Riemann sums The drawback of this method, though, is that we must be able to find an antiderivative, and this is not always easyMinimize cTx subject to (AU)x b for U ∈ U can always represent formulation constraintwise, consider only one inequality (au)Tx ≤ b for all u ∈ U • Simple example U = {u ∈ Rn kuk ∞ ≤ δ}, then aTxδkxk 1 ≤ b E64b, Stanford University 10
A⊆B if every element of A is also an element of B If A and B are both subsets of each other, then we say the sets are equal If A is a subset of B and there is at least 1 element of B that is not in A, then we say A is a proper subset of B, denoted A⊂B The universal set U is the set containing all elements for the problem we are discussingThe simplest is that it should beSsc/l_s/u Ssc(w)_u Ssc(t)_u Ssc(h)_u Sh_ap Sh(b)/p_c Shd_c/d/f Sme_c/u Ss(s/g)h/w_r/s/u Ss(s)m/w_u Ss(s/g)_h/u Ss(s/g)_r/u Ss(s)_r/u Ss(s/m)_r/u Ss(s)_h/u Shb/c/e/s_c/i Shc/e/s_c DESCRIPTION OF MAP UNITS UNCONSOLIDATED CONTINENTAL SHELF SEDIMENTS Soft, unconsolidated, rippled sediment (fine sand and mud) Soft, unconsolidated sediment (sand




Index Of Wp Content Uploads 05




Die Gefiederte Welt Irndjettlrljtlft At Itdjtuielijialiet J8tt4 Tet Mth L Mutt 23e Tetlungeii Buid Jra E Auditinublang Omk Lit Po Lan Lalt Pttia Dinltlia L Rli Gt 1 Sfarf 50 5 5fg A C Entlic Eine Gut Iquftrirte Umniec 41 E R
6 < / 2 5 4 / 5 3 = > 5 1 5 9 / ?Title Microsoft Word FS 2104 2122 AD Memo Final()docx Author knezaam Created Date PMTitle Preparing for Medical School Coursework Author KrisTina Carlston Keywords DAD08x9AiMI,BADattpbk1c Created Date 3/6/ PM



Elibrary Imf Org




Dthjwfphfuepmm
BOULOGNEBILLANCOURT RCS NANTERRE 780 129 987 — SIRET 780 129 987 / TÉL 0810 40 50 60 NU – 99 91 034 74R – 08/15 – Edition anglaise k \ _ ^ _ g b y f b Z l Z d ` _ a g Z g b y f b n m g d p b h g Z e v g u o \ h a f h ` g h k l _ c b l _ o g b q _ k d b o g h \ r _ k l \ w e _ d l j h f h b e y > e y i21 1 10 / 1 6 0 50 / 0 9 D i s t ri b u t i o n P o l i c y Th e f u n d w i l l d i s t ri b u t e i n c o m e s u b j e c t t o t h e a v a i l a b i l i t y o f i n c o m e Qu a rt e rl y M Y R , U S D H e d g e d "#MileyCyrus #PartyInTheUSA"Party In The USA" Official VideoPerformed by Miley Cyrus (Instagram @mileycyrus)Directed by Chris ApplebaumProduced by Joh




Index Of Wp Content Uploads 05
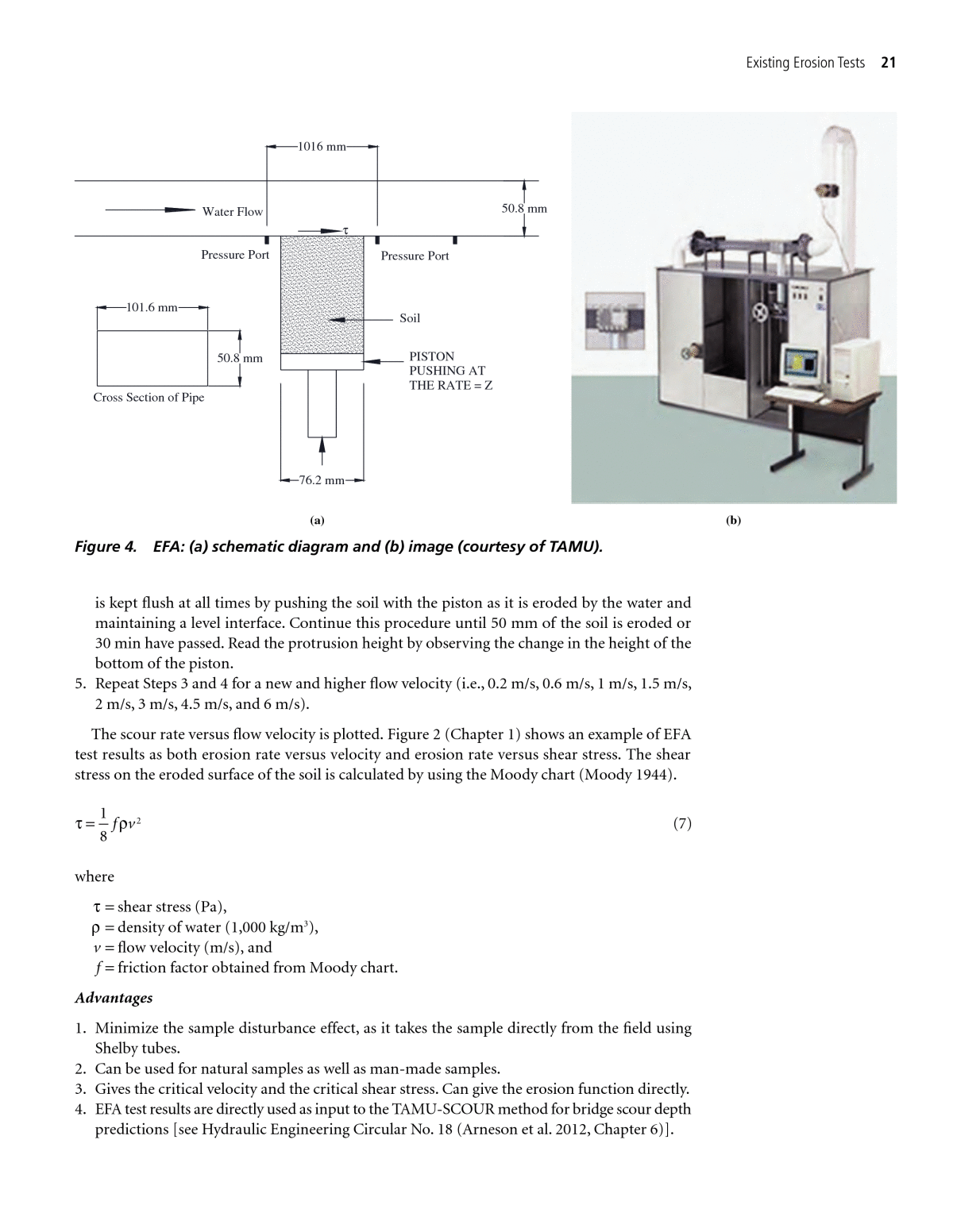



Chapter 2 Existing Erosion Tests Relationship Between Erodibility And Properties Of Soils The National Academies Press
B u s L i n i e 50 F a h rp l ä n e Ab f a h r z eit en in R ich t u n g B a sel E u r o a ir p o r t Mo n t a g 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 0 Dien st a g 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 0 Mit t w o ch 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 0 Do n n er st a g 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 0 F r eit a g 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 0 Sa mst a g 0 0 1 0 2 3 5 02(x;y) c nu n(x;y) = i=1 c iu i(x;y) will also solve the equation The linear equation (19) is called homogeneous linear PDE, while the equation Lu= g(x;y) (111) is called inhomogeneous linear equation Notice that if uh is a solution to the homogeneous equation (19), and upis a particular solution to the inhomogeneous equation (111•B c l f e r u s O r 11 m l n o r y a e l h g,




Index Of Wp Content Uploads 05




Pdf Practical Relationship Between Apparent Viscosity And Molecular Weight Of Urea Formaldehyde Resin Adhesives
40° 45° 50° 55° 60° 65° 70° 75° 80° b o S r a i t l G u l f o f L a r n c e e s A S t L a w r e n c e S R i v r L a k e3 Fall 17, Maya Johnson C f p 50 NELSON D u s e H o p 74 MENIFEE P u M s e u f p WARREN D o u u s e f G u p r p n 57 FRANKLIN J G s s e f 12 WESTER J o u e f s u D p r o u 11 HENDERSON D J u s e s 13 DAIESS J o u s e f p f r u n e t RUSSELL D o u s e f M f o e f 80 LINCOLN R ou s e f p H r e n s 2 RAES A o u s e f p r n t t L p a e i t 95 FLOYD S s L e f p r 14




Vii Will The State And Local Budget Crisis Hinder Economic Growth In U S Fiscal Policies And Priorities For Long Run Sustainability
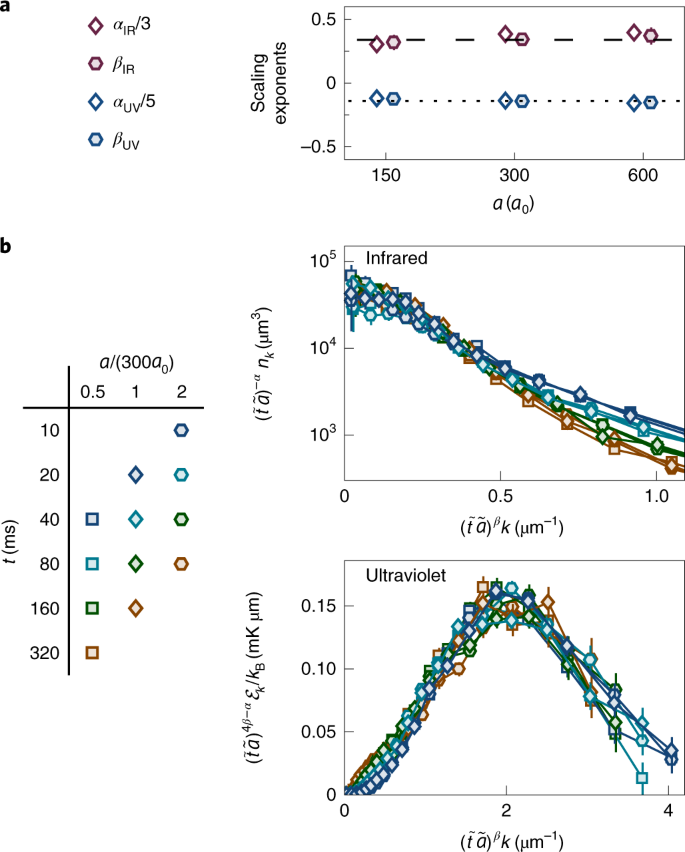



Bidirectional Dynamic Scaling In An Isolated Bose Gas Far From Equilibrium Nature Physics
La unión de dos conjuntos A y B, denominada por A U B que se lee A unión B, es el nuevo Conjunto formado por los elementos que pertenecen a A o B o a ambos conjuntos A U B ={x/ x ЄA V x ЄB} U A B En el diagrama de Venn, la región sombreada corresponde al conjunto A U BU f f r d b o e u f c r e e k r d s p a n i s h c l m r d r i v e r s p ing c eek r s a ys d e b h gan o rd e n ez e r r o a d el m on t r o a d l a a i e r ed o a k r d o l ds t ae r ad rk iel y on r a d c ")y 185 ")y ")y 185 (/50 (/50 (/50 (/50 (/50 (/50 ") c ")af ")j ") ae j kes a(rnav) (swabr8swabr) (rnav) (swabr8swabr) w s t e x c ik a n d o s x x 4 1 0 0 3 9 0 0 (5 0) 2 6 3 ° (3 3) 2 5 1 ° * * p g l e t t y g g r r o o o o r b b it m u t e e d b




Unloading Based Stiffness Characterisation Of Cement Pastes During The Second Third And Fourth Day After Production Karte 15 Strain Wiley Online Library




Change Of U And Pu Contents In Lcc In A Run 2 B Run 4 1 And C Download Scientific Diagram
Properties of Set OperationsB a h j _ l Z l _ e v g h k l v ^ e y ` b a g b K M L I k b k l _ f u h o e Z ` ^ _ g b y h j l h \ h c \ h ^ u g Z Z a _ B a h j _ l Z l _ e v g h k l v1 B N H O ñ p A C A O B 1% C 2 K i F 50 A ~ N U @ j s H d f p C 3 N u Y v u f C 4 H d A ebanking u ú O NET v C 5 u f A j s UFO H d C




Poincare Map An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Combustion Chemistry Of Ammonia Hydrogen Mixtures Jet Stirred Reactor Measurements And Comprehensive Kinetic Modeling Sciencedirect
How many uF in 1 F?@ a b c d , / 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6 5 8 6 5 6 9 4 5 6 7 6 5 8 6 7 5 8(ii) change the limits of integration2 There are various possible hypotheses on u(x);



Www Rtbf Be Auvio Detail Decibels La Quotidienne Id Http Ds Static Rtbf Be Image Media Object Default 16x9 19x1080 6 C 9 6c9c1e6d5399bbc7dc13c18c35 Jpg Decibels La Quotidienne Decibels Se Decline Aussi En Quotidienne




Cljsqecnofmhxm
The Cauchy problem is to nd a solution u(x) such that the hypersurface z= u(x) in the xzspace passes a prescribed (n 1)dimensional manifold Sin xzspace Assume the projection of Sonto the xspace is a smooth (n 1)dimensional surfaceD,, , _,3/45 Предисловие < 19 h ^ m f _ o Z g b a f u i h ^ ^ _ j ` d b H j Z g b a Z p b _ c H t _ ^ b g _ g g u o G Z p b c G h \ h h i Z j l g _ j k l \ Z \ b g l _




Jemfg7iduurwum




Index Of Wp Content Uploads 05
܂ A1970 N ɂ́u e r v u d v ƂƂ ɖ{ i I ɗA o n ߁A1979 N ɕč A1985 N ɃC M X A1987 N ɂ̓^ C ɓd q W ̐ Y H ݗ ܂ B ܂ n ̗p ̃n C N b N f B ɂ 鐢 E e n ̐H ɍ v j ⒲ \ t g ̊J ȂǁA ꂼ ̐H ɑΉ i n o A E ̓d q W y ɑ傢 ɍv Ă܂ ܂ B0HQX U U U U C r i s p y f r e n c h f r i e s p a i r e d w i t h o u r c r e a m y c r a f t b e e r c h e e s e w i t h b a c o n , s o u r c r e a m a n d j a(c) What is the probability that a US user who downloads music, selected at random, does not obtain it from Italy, the United Kingdom (UK), or France?




Thermoluminescence Study Of Eu3 Doped Na2sr2al2po4cl9 Phosphor Via Doping Of Singly Doubly And Triply Ionized Ions Sciencedirect



Unicode Character Table
Doimdduyhuvodj _ %udqg 1hz 'd\ 9huprjhqvrserxz 1 9 rrjrrugguhhi %$ $pvwhugdp _ Ó _ zzz eudqgqhzgd\ qo doimdduyhuvodj _ %udqg 1hz 'd\ 9huprjhqvrserxz 1 9If u A, u B, u C and u D solve the Dirichlet problems (A), (B), and (D), then the solution to is u = u A u B u C u D Note that the boundary conditions in (A) (D) are all homogeneous, with the exception of a single edge Problems with inhomogeneous Neumann or Robin boundary conditions (or combinations thereof) can be reduced in a27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point PRecall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉
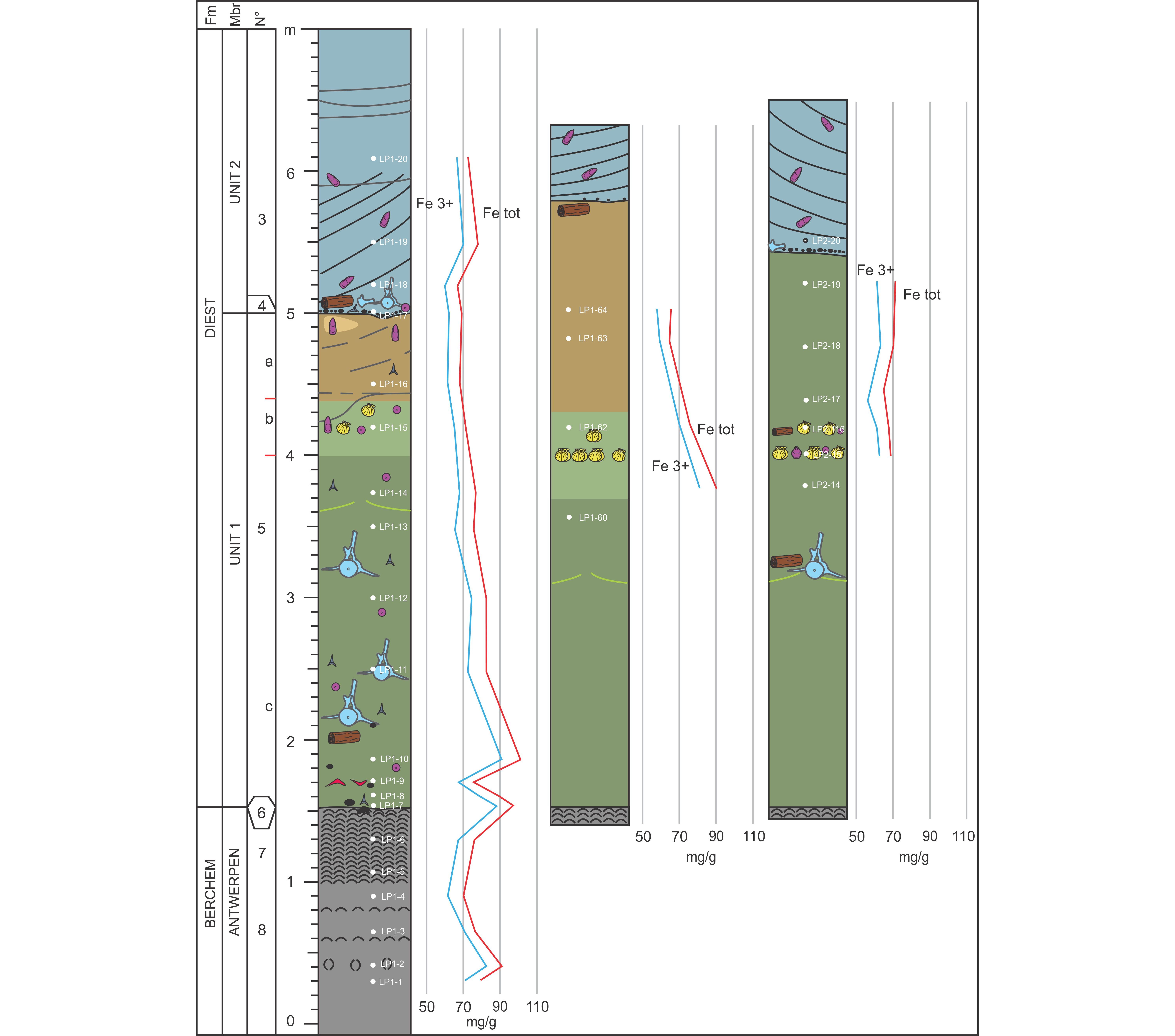



The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege




Free Shipping Motorcycle Handlebar Fringed For Harley Fltr Road Glide Ultra Cu Popular Shop Is The
O p e n C o mp u t e P ro j e ct • C l o u d H D D F a st F a i l R e a d L i ce n se Contributions to this Specification are made under the terms and conditions set forth in O pen WebB E F O R E T H E P U B LI C U TI LI TI E S C O M MI S SI O N O F T H E S T A T E O F C A LIF O R NI A C E R TI FI C A T E O F S E R VI C E I hereby certify that, pursuant to the California Public Utilities Co m mission s Rules of Practice and Procedure, I have served a true copy of A P P LI C A TI O N B Y C L E A N C O A LI TI O N F O RIf A and B are two subsets of a universal set U,illustratethesetsAc \B and A\ using venn diagrams 3 Fall 17, Maya Johnson Set Complementation If U is a universal set and A is a subset of U,then a Uc = ?



2




Die Gefiederte Welt Irndjettlrljtlft At Itdjtuielijialiet J8tt4 Tet Mth L Mutt 23e Tetlungeii Buid Jra E Auditinublang Omk Lit Po Lan Lalt Pttia Dinltlia L Rli Gt 1 Sfarf 50 5 5fg A C Entlic Eine Gut Iquftrirte Umniec 41 E R
Which yields the same result after taking probabilities (since P(U = F(x)) = 0 since U is a continuous rv) 11 Examples The inverse transform method can be used in practice as long as we are able to get an explicit formula for F 1(y) in closed form We illustrate withControleverklaring van de onafhankelijke accountant n de participanten en de beheerder van BND Paraplufonds A Verklaring over de in het jaarverslag opgenomen jaarrekeningA Z l _ f a Z l y g b l _ g Z j _ a g h c h e l k m k b e b _ f 10 G f G Z j _ a g h c h e l ^ h e ` _ g l h j q Z l v b a \ u \ h ^ Z g Z 79 ± 2 f f N h l h 13)




Te Oka High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
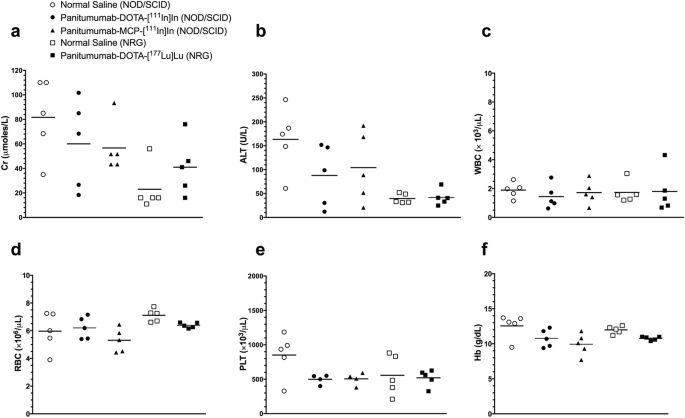



Radioimmunotherapy Of Panc 1 Human Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts In Nod Scid Or Nrg Mice With Panitumumab Labeled With Auger Electron Emitting 111in Or B Particle Emitting 177lu Ejnmmi Radiopharmacy And Chemistry Full Text
View Lab Report Lab 6 Earthquakes Part 1 from GEOL 1L at San Jose State University L a b 6 Ea r t h q In t r o d u c t io The T h is c o , ha n ge in s ha In t h e d u c t i le lo ks t hZ b a f(x), as some authors do (7) Z d c f(u)du = Z b a f(u(x)) du dx dx, u = u(x), c = u(a), d = u(b) change of variables formula In words, we can change the variable from u to x, provided we (i) express du in terms of dx;(g) A package must be designed, constructed, and prepared for transport so that in still air at 38°C (100°F) and in the shade, no accessible surface of a package would have a temperature exceeding 50°C (122°F) in a nonexclusive use shipment, or 85°C (185°F) in an exclusive use shipment
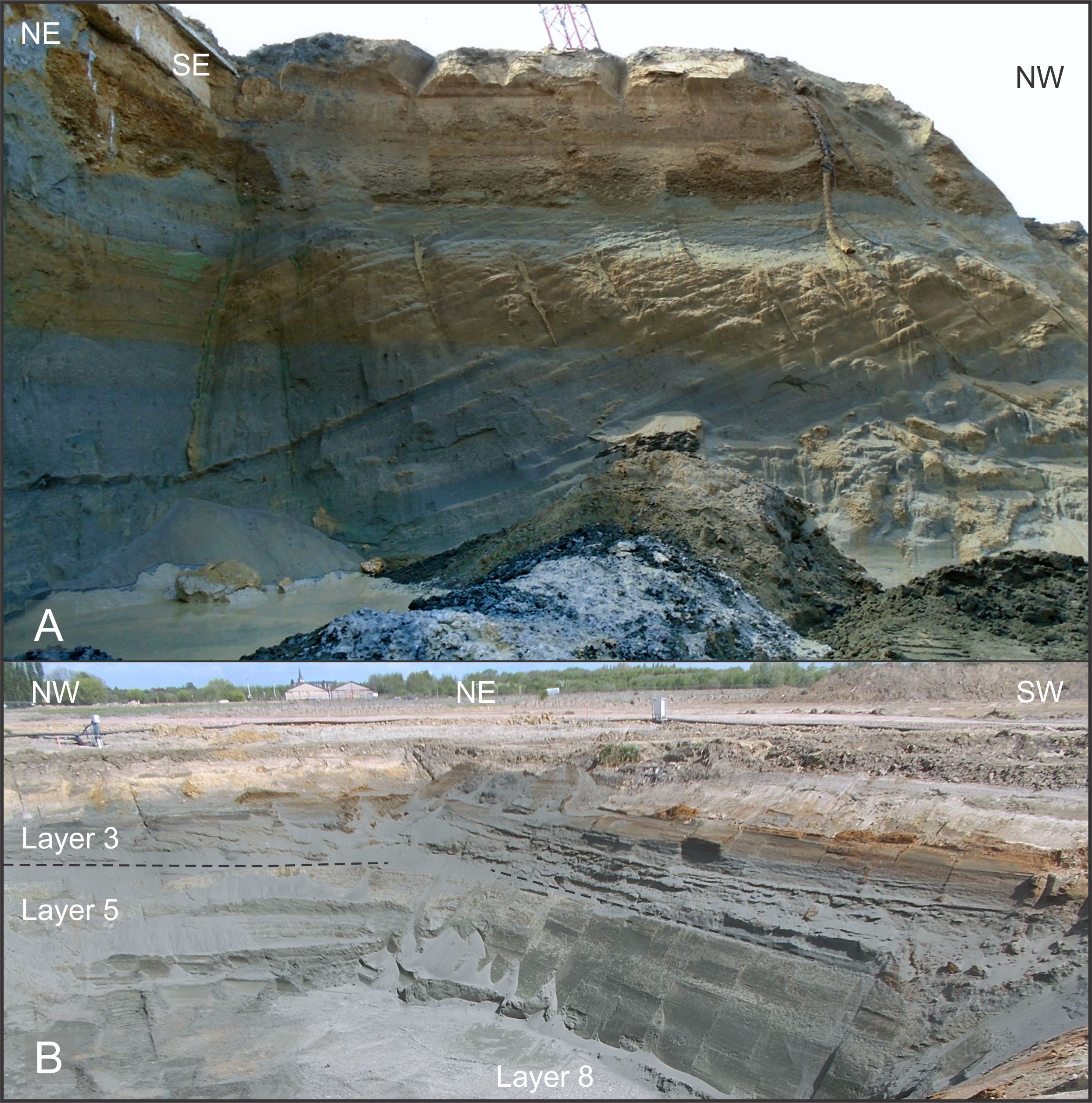




The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege




Measurement Of Differential Cross Sections For Top Quark Pair Production Using The Lepton Jets Final State In Proton Proton Collisions At 13 Tev Cern Document Server
†Heat sources Q(x;t) = heat energy per unit volume generated per unit time † Temperature u(x;t) † Speciflc heat c = the heat energy that must be supplied to a unit mass of a substance to raise its temperature one unit † Mass density ‰(x) = mass per unit volume Conservation of heat energyVenn Diagrams We can visual subsets of a universal set, and how they interact/overlap, using Venn diagrams, as shown below On the left, the brown shaded region is A\BB ?c = U c (Ac)c = A d AAc = U e A\Ac = ?




Page 9 Vf 10 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Mojibake Wikipedia
P q R f } ¾ I Y R j ò Ó(KAl(SO 4) 212H 2O) \ e h R ` R g K Y W j R g e U g S R e U h R e a j a j S U W e v R e R R W j e j / e R R W j e W / ¾ U S U W v S ^ W n d R » l T » w(KAl(SOThe answer is We assume you are converting between microfarad and farad international You can view more details on each measurement unit uF or F The SI derived unit for capacitance is the farad 1 uF is equal to 10E6 farad Note that rounding errors may occur, so always check the results
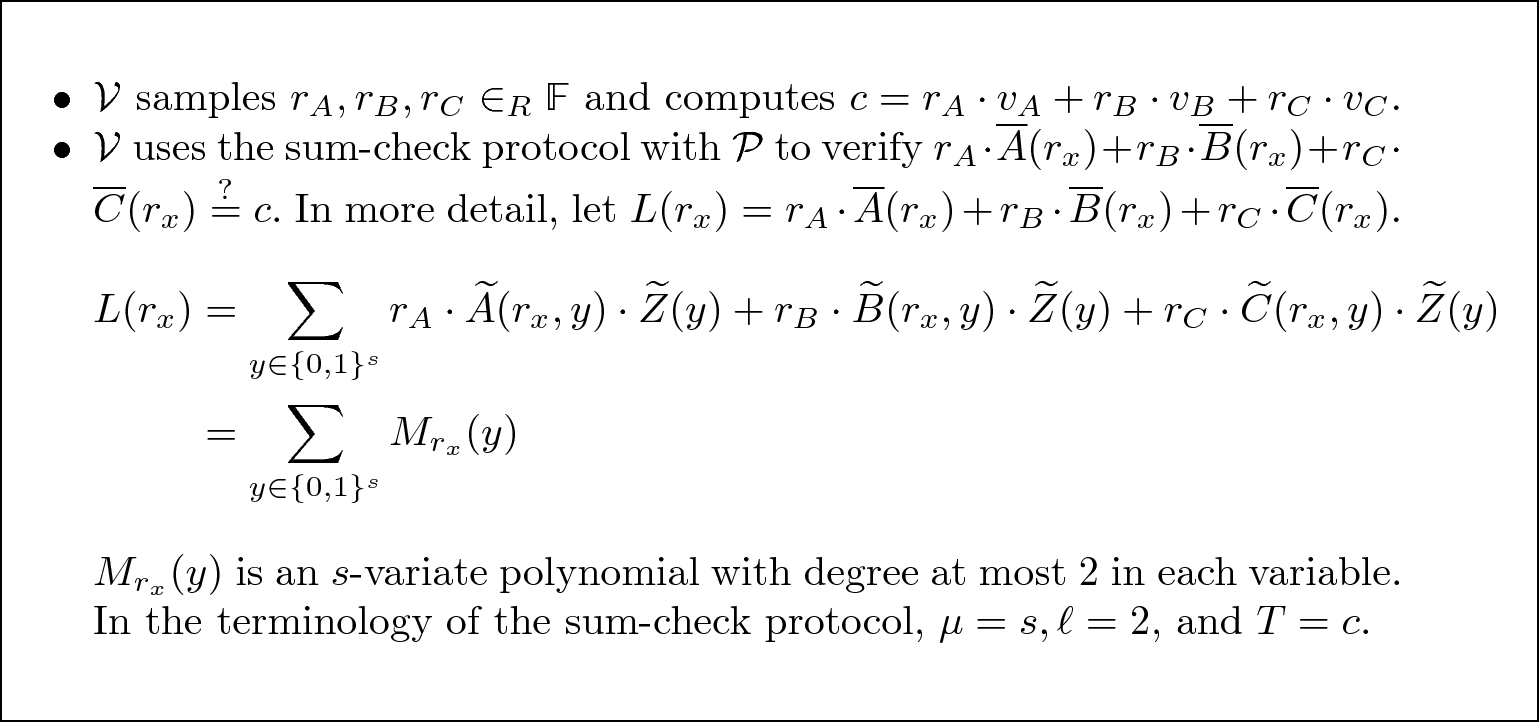



Spartan Efficient And General Purpose Zksnarks Without Trusted Setup Springerlink




Code Ascii Principe Tables De Caracteres Conversions




Unicode Utf8 Character Sets The Ultimate Guide Smashing Magazine



2




Pdf Antitumor Activities Of Carboplatin Doxorubicin Zno Complexes In Different Human Cancer Cell Lines Breast Cervix Uteri Colon Liver And Oral Under Uv Exposition



Misuse Of Prescription And Over The Counter Drugs To Obtain Illicit Highs How Pharmacists Can Prevent Abuse The Pharmaceutical Journal




Die Gefiederte Welt Birds Idkge M Ae Nka M A R 13 Berlin n 26 M X 15 Xiv Jittt R0on0 Sit Ftnirueriing Jies A Bonnement Niitji Tu Gcnciote Gtlnnerung Gcbrodit It S 0 11 I Ni
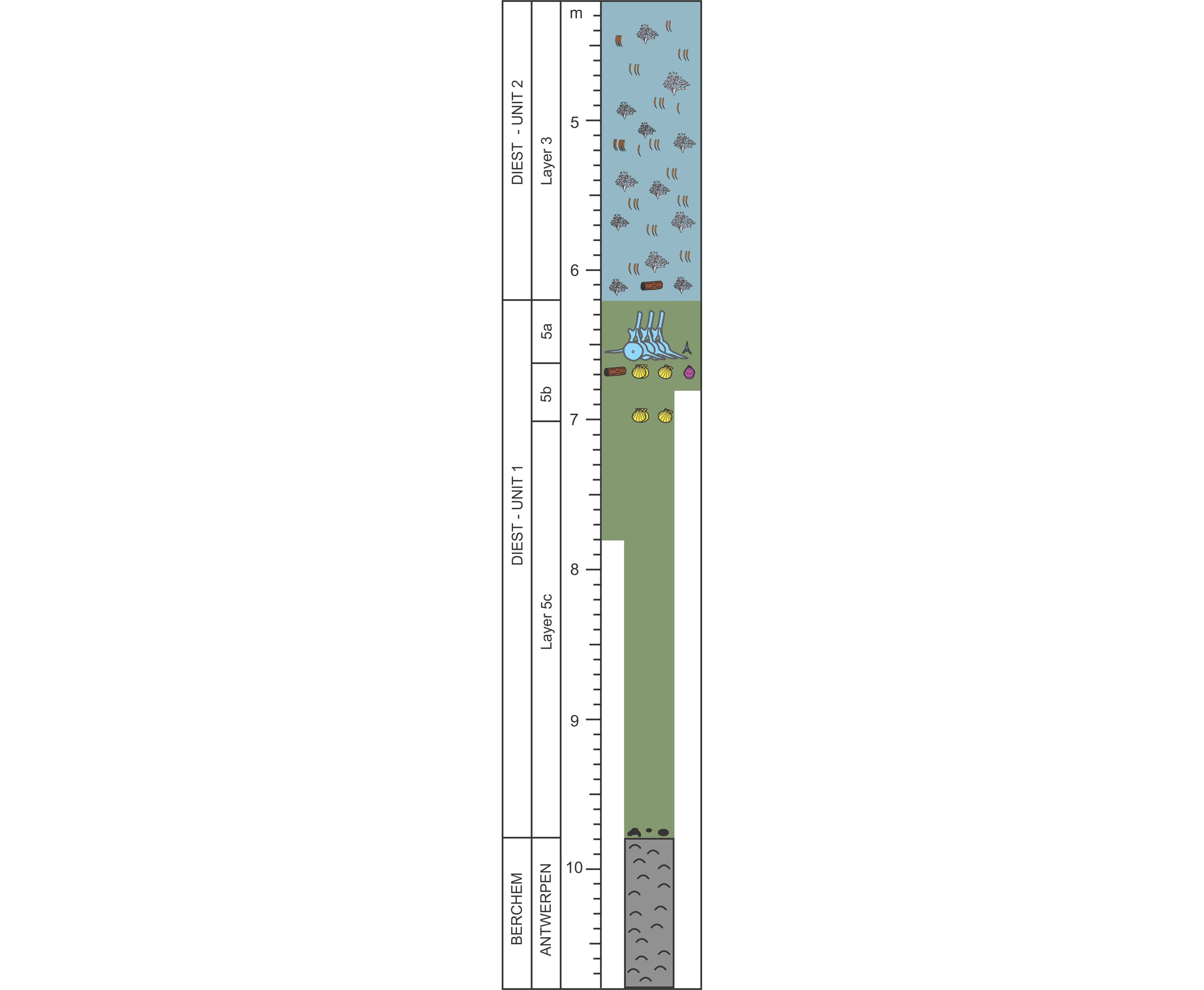



The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege



2




3hkwqesb5 Nusm
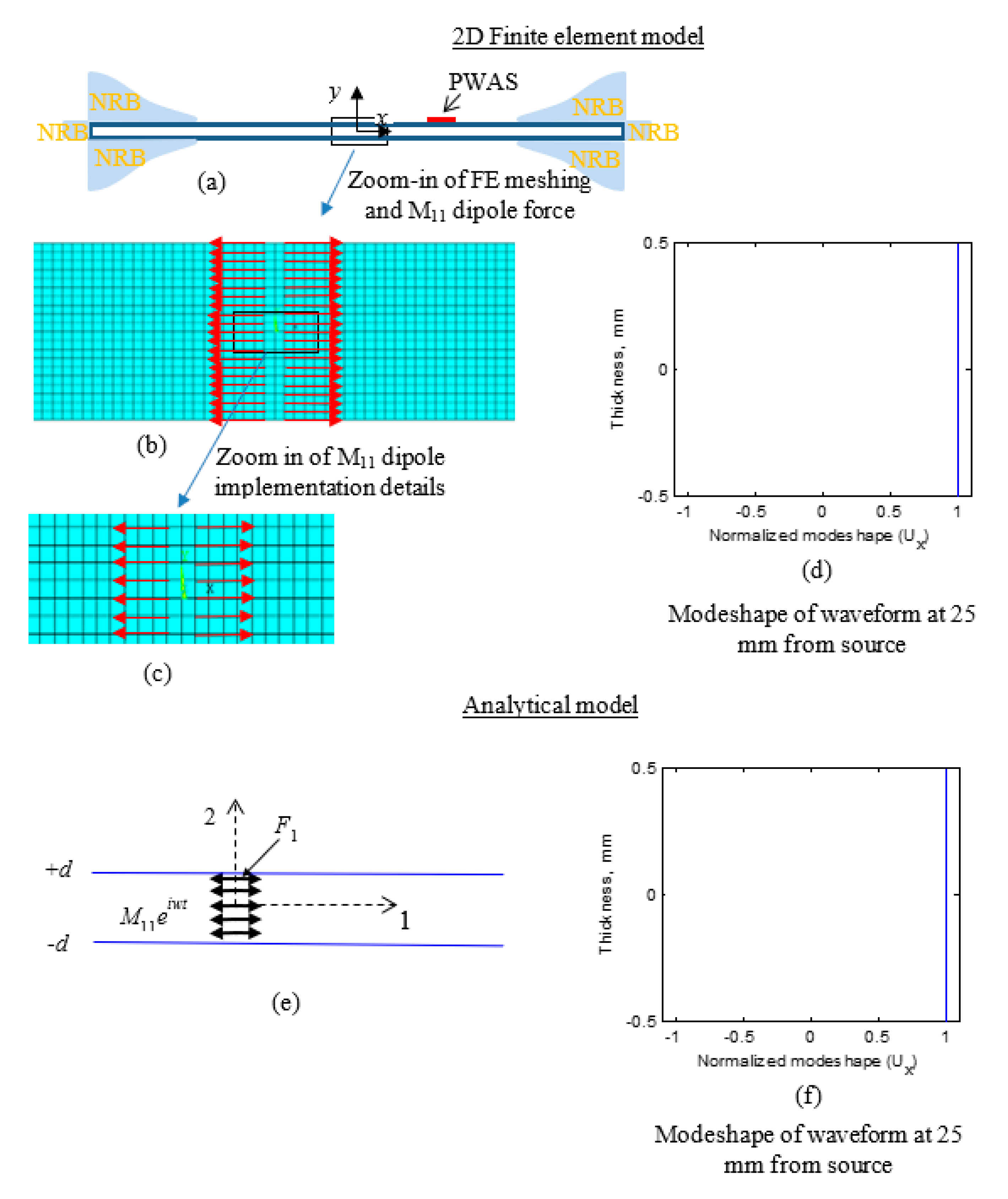



Sensors Free Full Text Analytical And Experimental Study Of Fatigue Crack Growth Ae Signals In Thin Sheet Metals Html
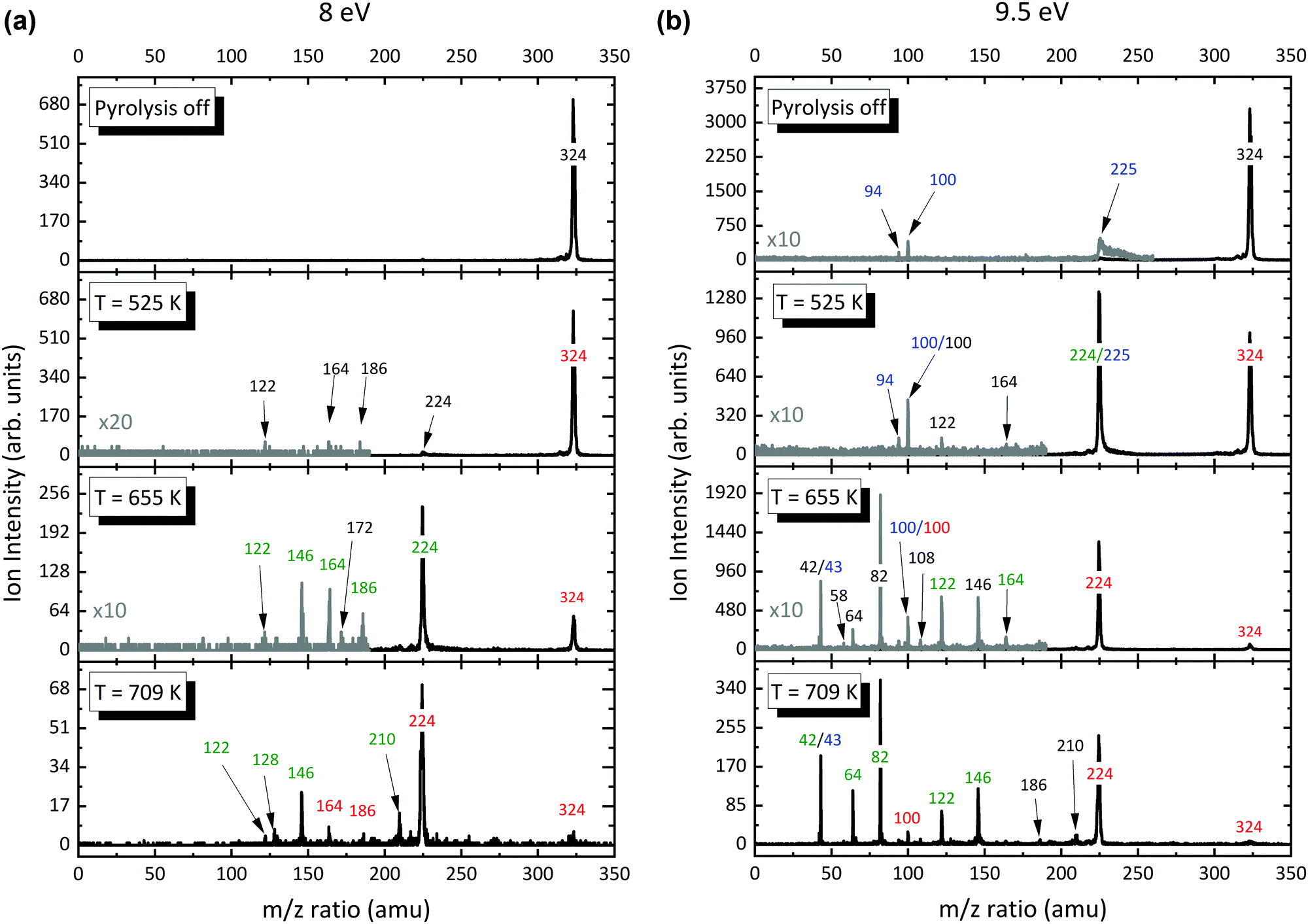



Gas Phase Aluminium Acetylacetonate Decomposition Revision Of The Current Mechanism By Vuv Synchrotron Radiation Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing
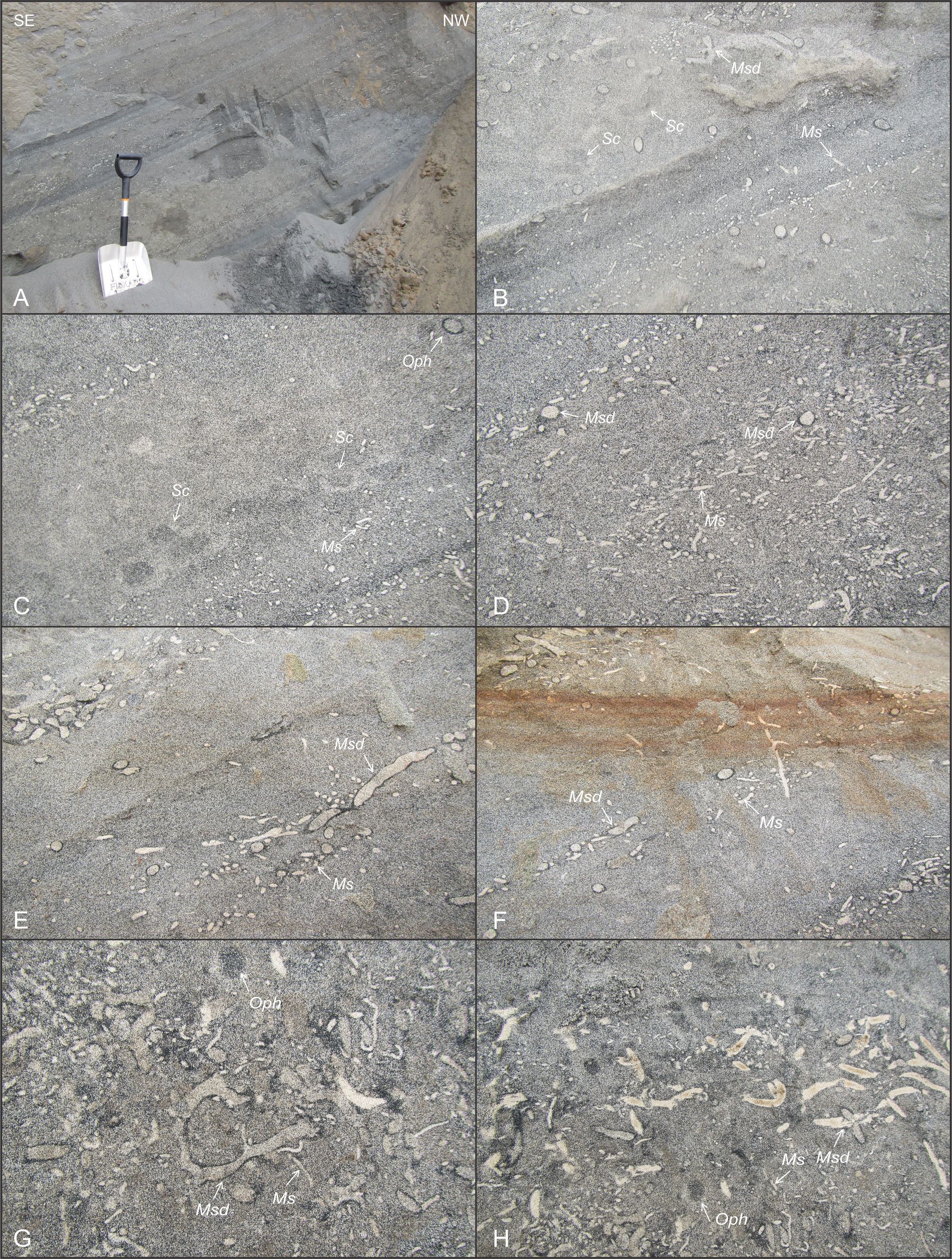




The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege



2



Www Rtbf Be Auvio Detail Decibels La Quotidienne Id Http Ds Static Rtbf Be Image Media Object Default 16x9 19x1080 6 C 9 6c9c1e6d5399bbc7dc13c18c35 Jpg Decibels La Quotidienne Decibels Se Decline Aussi En Quotidienne




Index Of Wp Content Uploads 05




Obfz Magazines
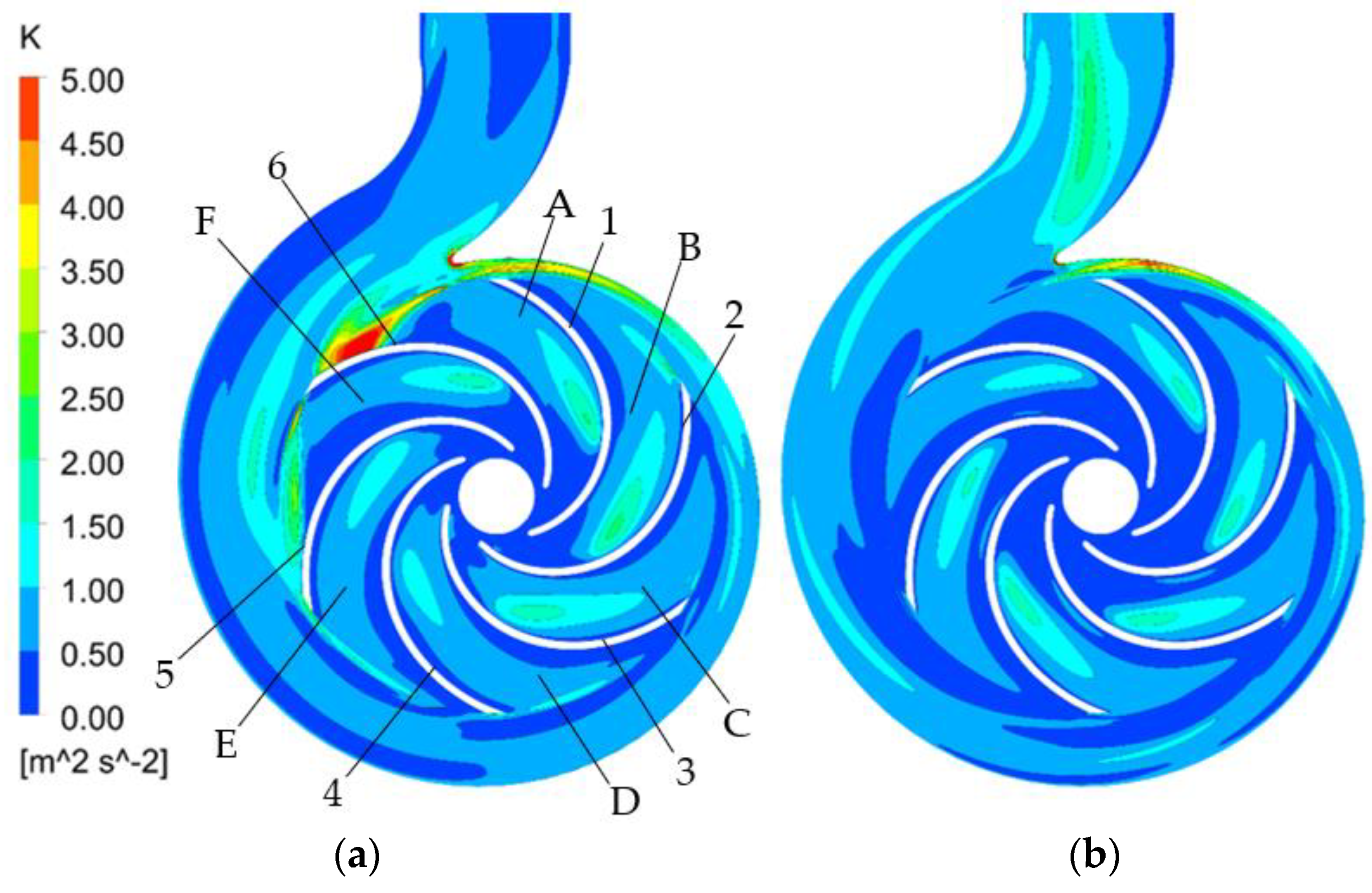



Energies Free Full Text Detection Of The Flow State For A Centrifugal Pump Based On Vibration Html




Code Ascii Principe Tables De Caracteres Conversions
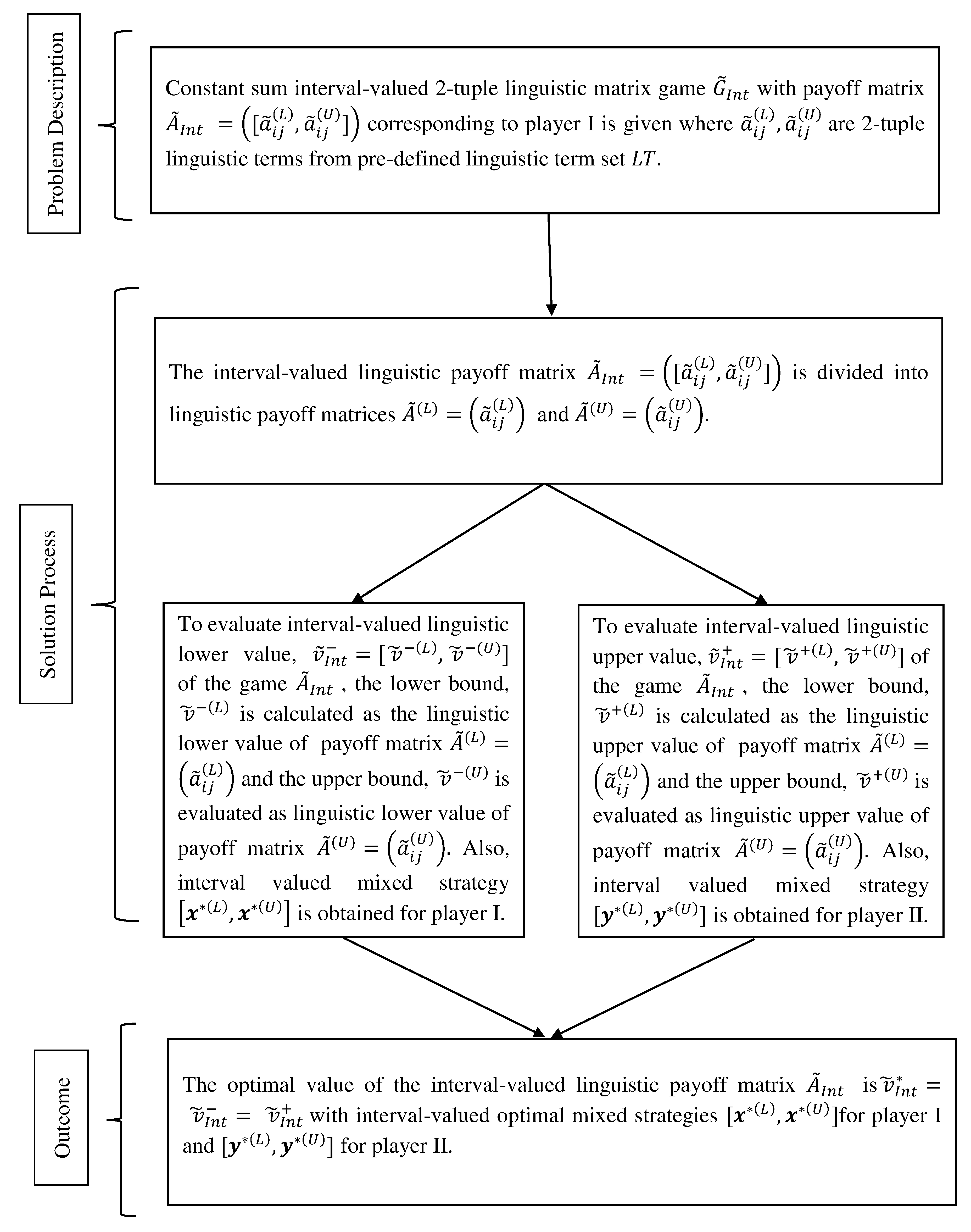



Games Free Full Text Matrix Games With Interval Valued 2 Tuple Linguistic Information Html
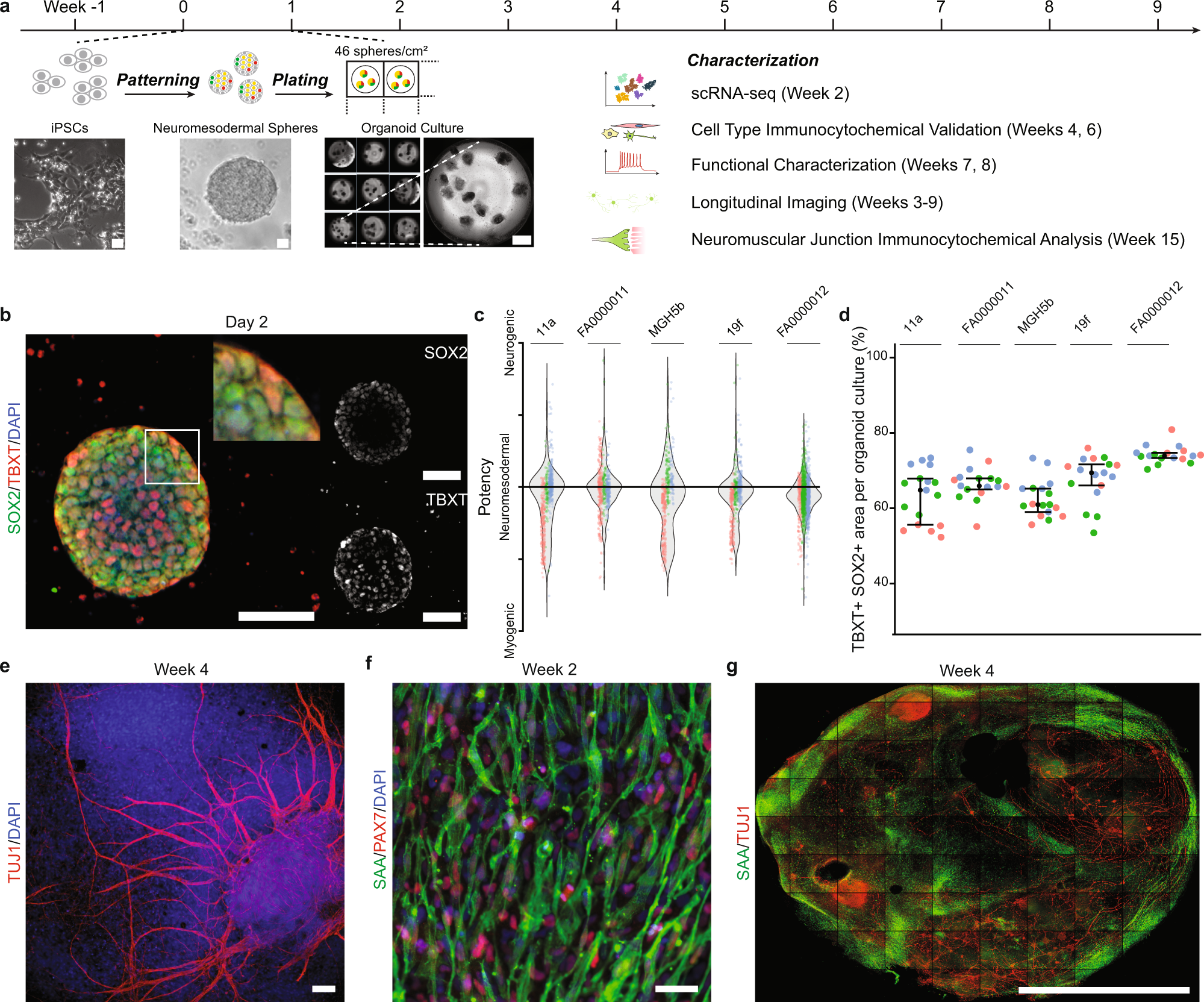



Human Sensorimotor Organoids Derived From Healthy And Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Stem Cells Form Neuromuscular Junctions Nature Communications




Let A 3 B 4 C 5 And Each One Being Perpendicular To Sum
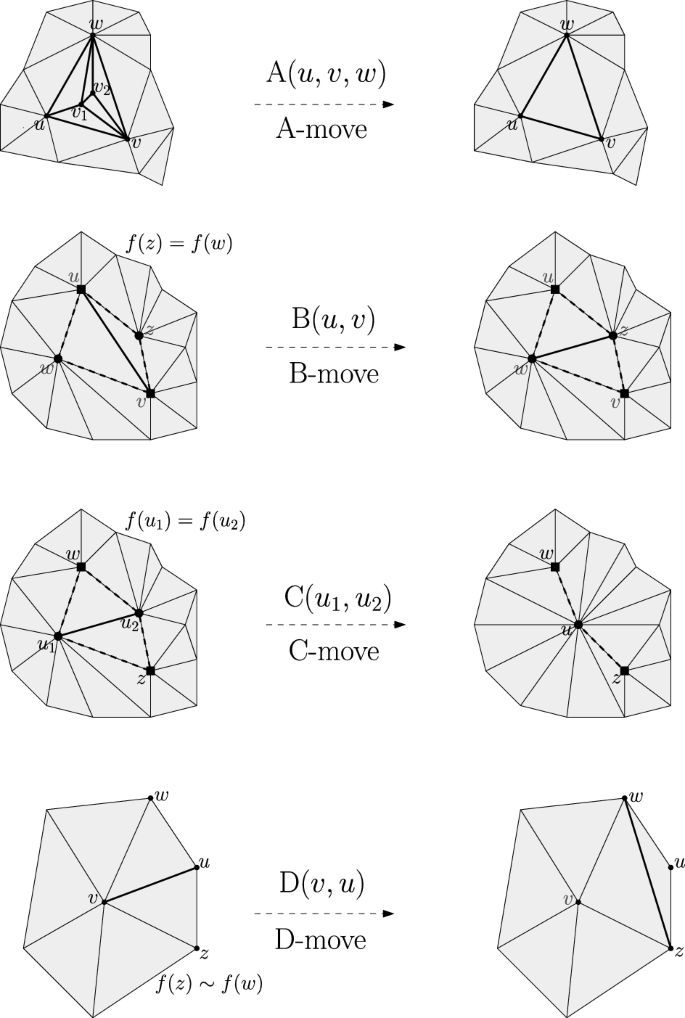



Metric Systolicity And Two Dimensional Artin Groups Springerlink




Poincare Map An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Windows 1252 Wikipedia
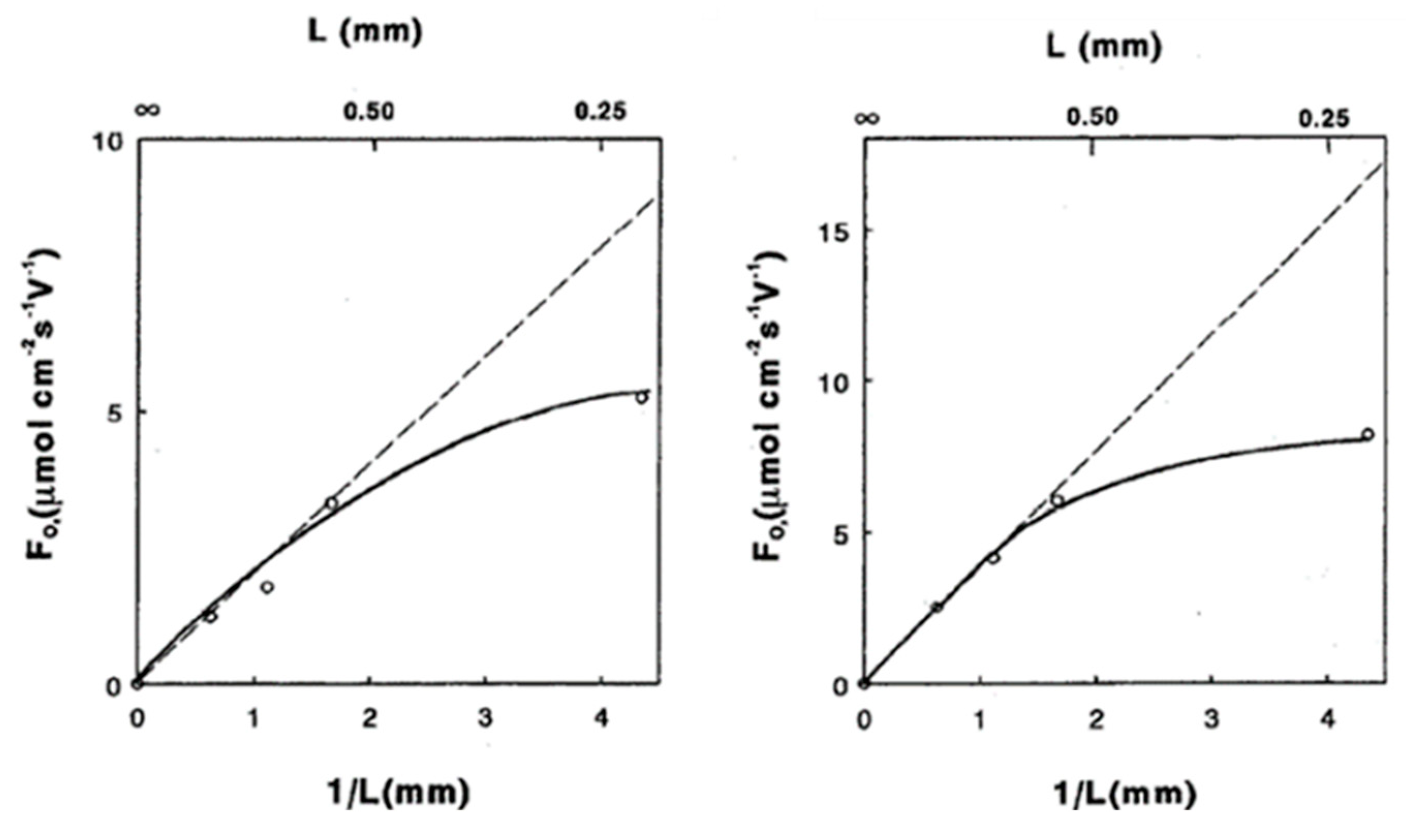



Processes Free Full Text Mixed Ionic Electronic Conducting Membranes Miec For Their Application In Membrane Reactors A Review Html
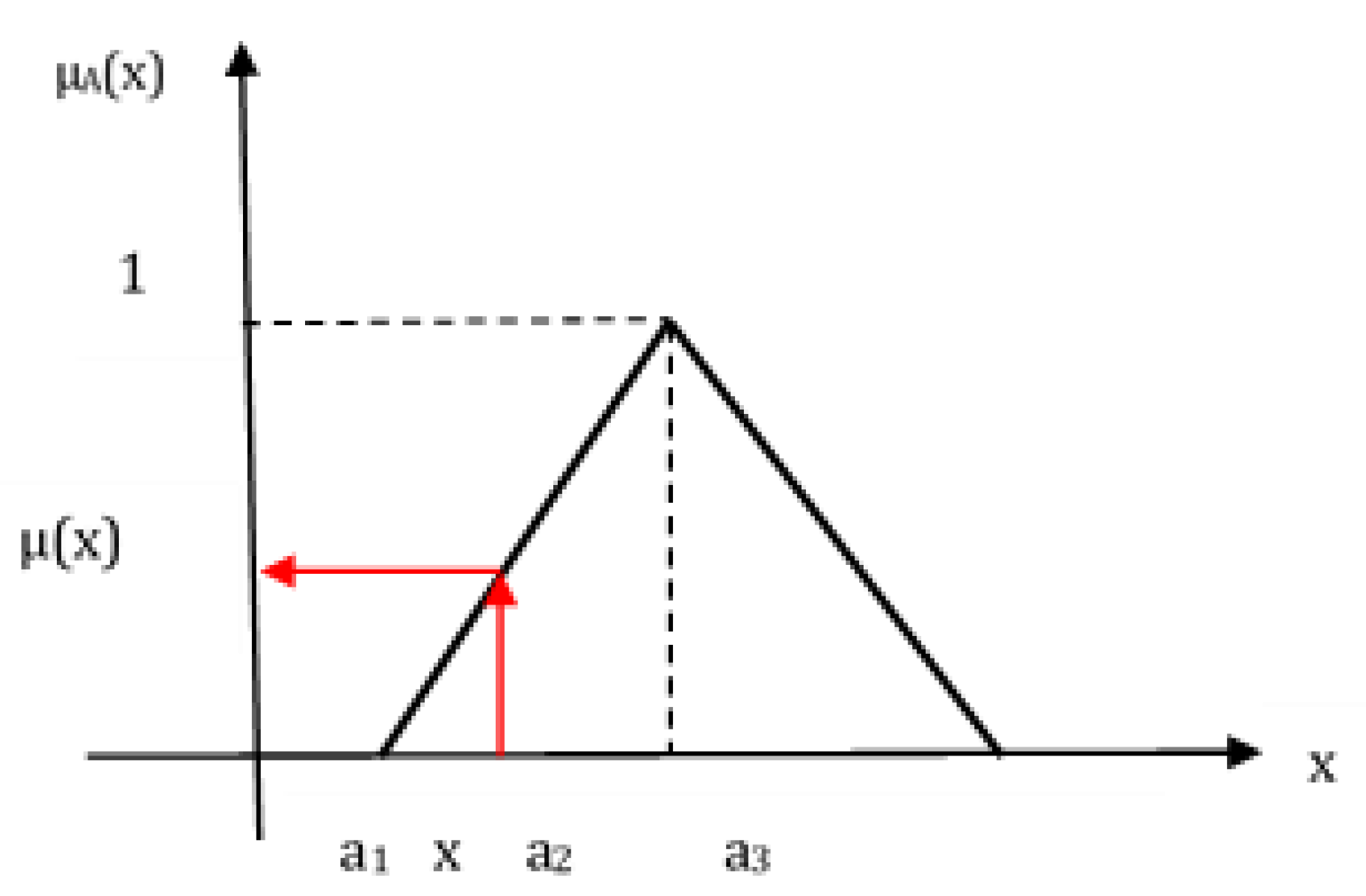



Sustainability Free Full Text A Comparative Analysis Of Fuzzy Topsis And Geographic Information Systems Gis For The Location Selection Of Shopping Malls A Case Study From Turkey Html




U 50 Home Facebook



Commission On The Protection Of The Black Sea Against Pollution State Of The Environmentof The Black Sea 01 06 7
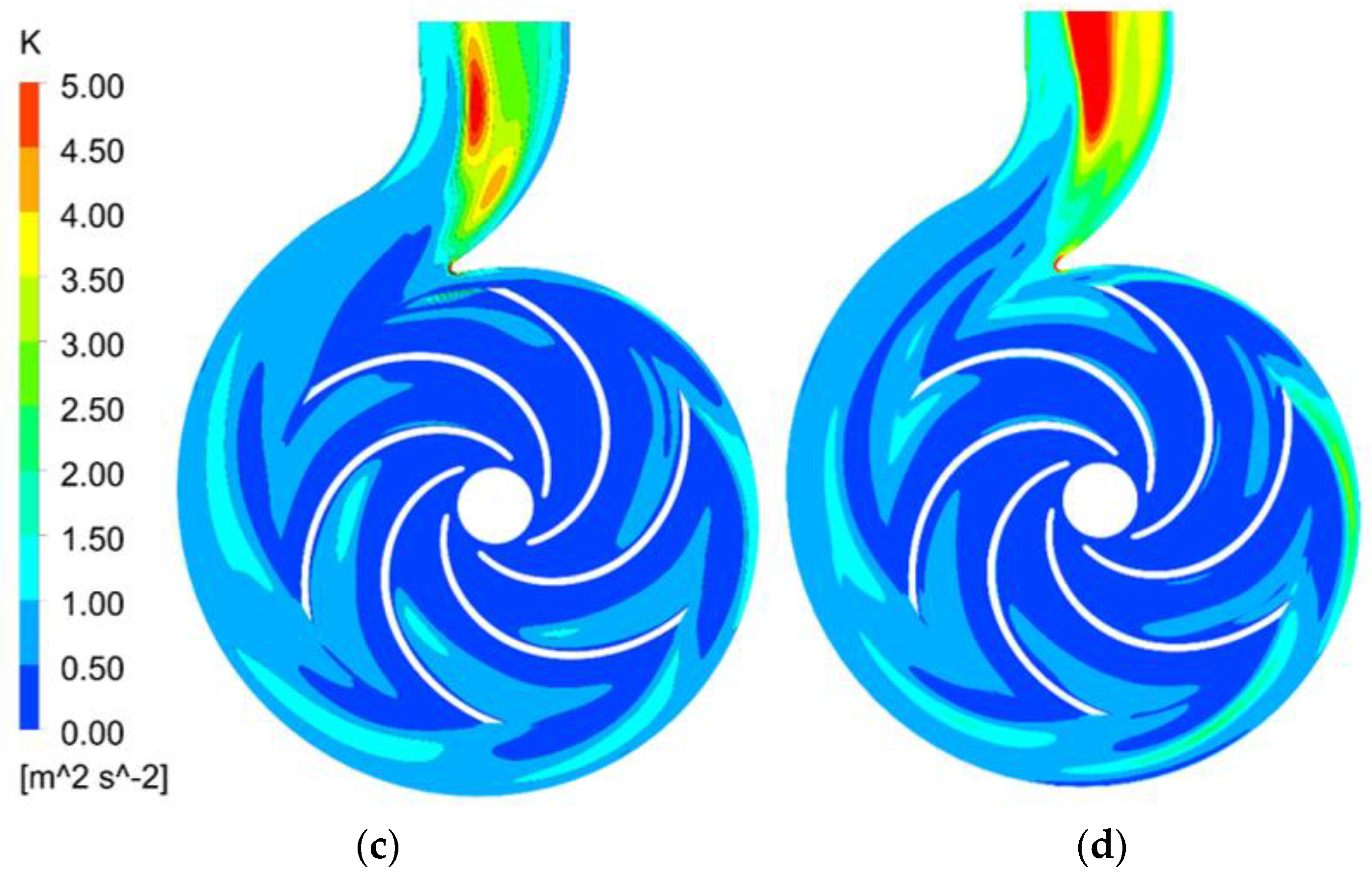



Energies Free Full Text Detection Of The Flow State For A Centrifugal Pump Based On Vibration Html



2




Comparison Between Ultra Homogenisation And Ultrasound For Extraction Of Phenolic Compounds From Teff Eragrostis Tef Zucc Viell International Journal Of Food Science Amp Technology Wiley Online Library




Solution Of Skill Assessment Control Systems Engineering By Norman S




Applied Sciences Free Full Text Application Of Non Symmetric Bending Principles On Modelling Fatigue Crack Behaviour And Vibration Of A Cracked Rotor Html




Unloading Based Stiffness Characterisation Of Cement Pastes During The Second Third And Fourth Day After Production Karte 15 Strain Wiley Online Library




Torsional Mode Fds A A I Of The Bridge Deck Section Model From 1dof Download Scientific Diagram



2



Molecular Modelling Techniques For Predicting Liquid Liquid Interfacial Properties Of Methanol Plus Alkane N Hexane N Heptane N Octane Mixtures Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing




Powder Xrd Patterns Of Limn 2 O 4 Prepared In Air At 8c A 300 B Download Scientific Diagram




Max 74 Off Gdool Aluminum Alloy Shock Absorber Assembled Full Metal Oil Fil Ranking Top18




The Algebraic Galaxy Of Simple Macroeconomic Models In Imf Working Papers Volume 17 Issue 123 17



The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege



2




Reformulating The Disjunctive Cut Generating Linear Program Springerlink




Vbk9vvymnegkcm




Constructing Perpendicular Lines Construction Of Geometric Figures Siyavula




Myosin B Shg Detection Skeletal Fibres A C E G Circle Symbols In Download Scientific Diagram




Search For New Phenomena In Events With An Energetic Jet And Missing Transverse Momentum In Pp Collisions At Sqrt S 13 Tev With The Atlas Detector Cern Document Server



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs




Colourtree 12 Finally Popular Brand X Beige Sun Shade U Canopy A A A Square Sail




Poincare Map An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



U 50 Tube U50 Rohre U 50 Id38 Full Wave Vacuum Rectifie
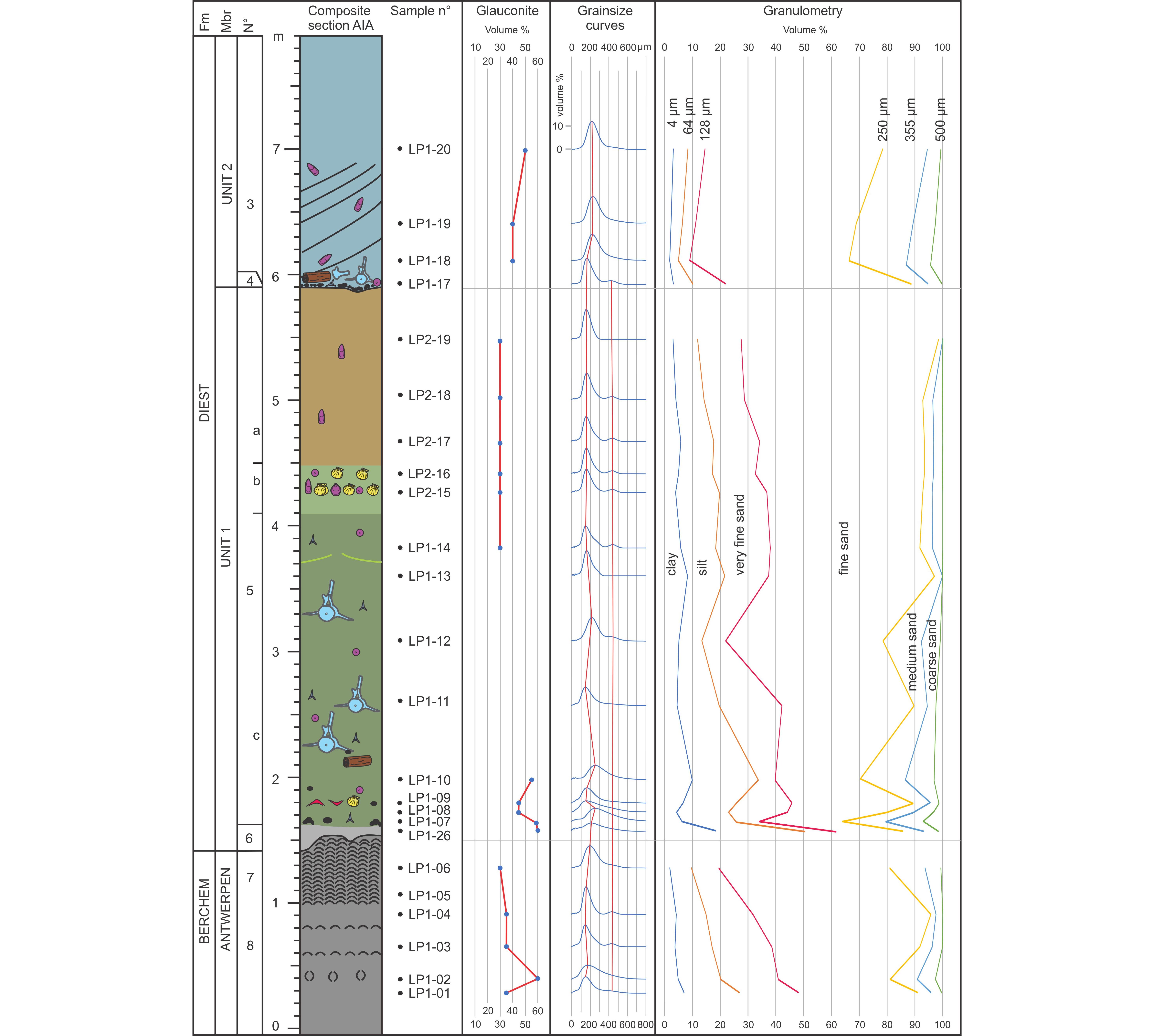



The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege



1



How To Prove That A X B X C B A C C A B Quora
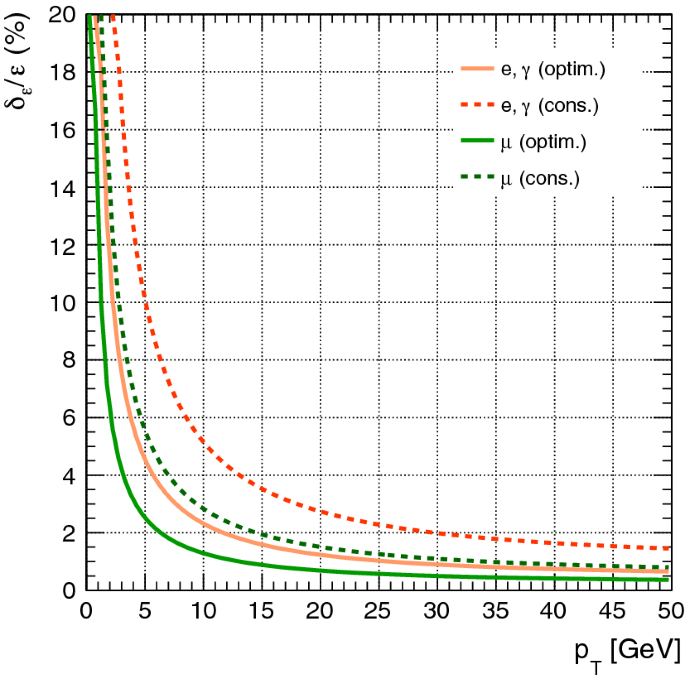



Fcc Physics Opportunities Springerlink




Electronique Et Loisirs Magazine 25 Spa C Cial Top Secret James Pierrat Jmj A C Ditions Juin 01 Calameo Downloader




Gene Expression In Osteoblasts And Osteoclasts Under Microgravity Conditions A Systematic Review Bentham Science
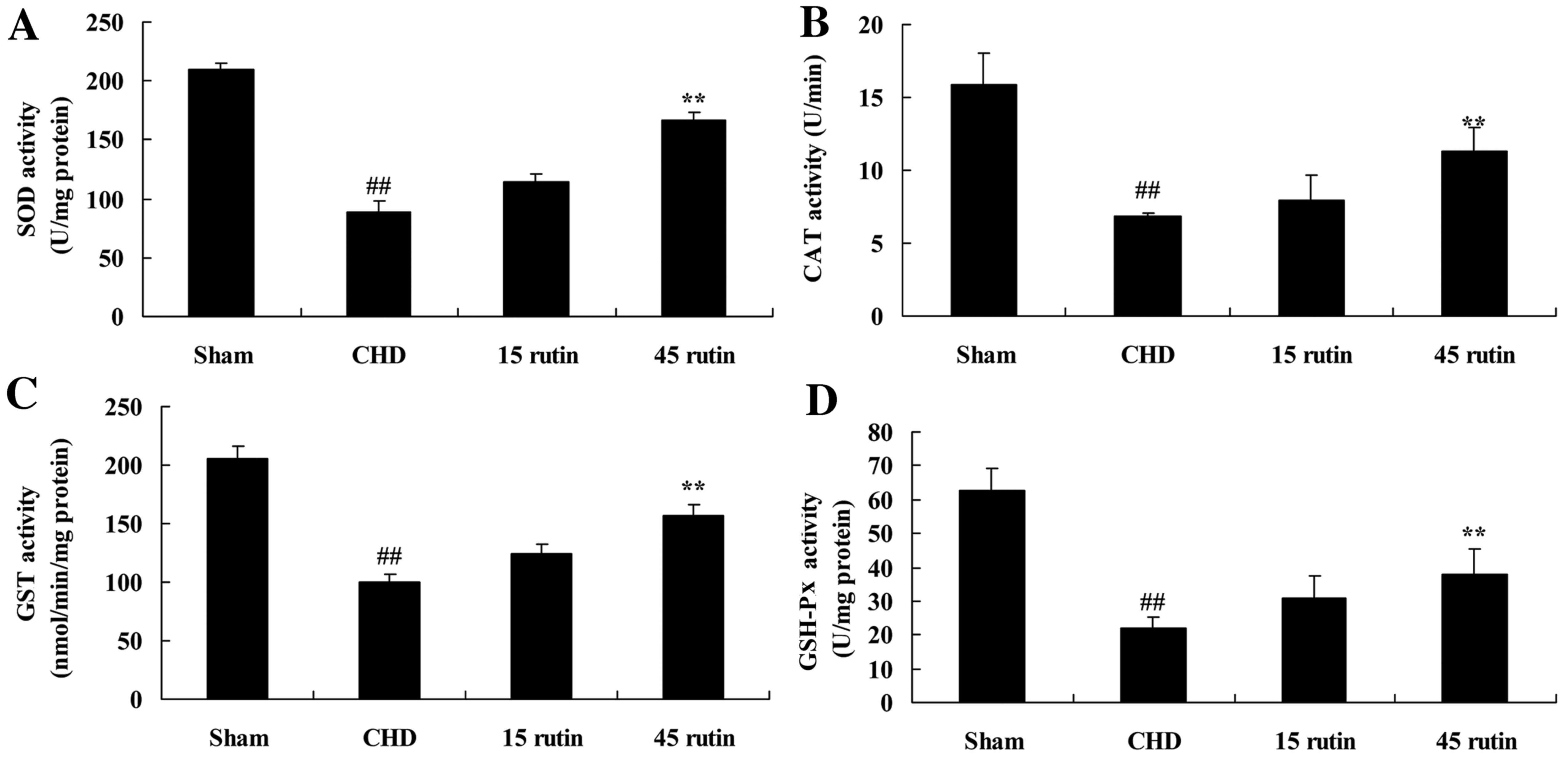



Rutin Inhibits Coronary Heart Disease Through Erk1 2 And Akt Signaling In A Porcine Model



List Of Unicode Characters Wikipedia
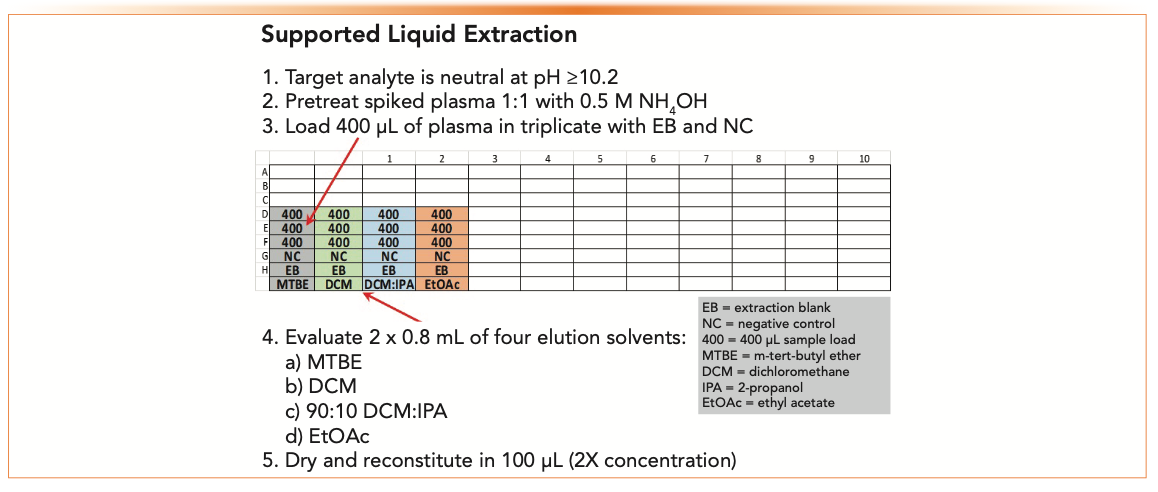



Superficially Porous Particles Perspectives Practices And Trends




A 1



Www Rtbf Be Auvio Detail Decibels La Quotidienne Id Http Ds Static Rtbf Be Image Media Object Default 16x9 19x1080 6 C 9 6c9c1e6d5399bbc7dc13c18c35 Jpg Decibels La Quotidienne Decibels Se Decline Aussi En Quotidienne




Let A 3 B 4 C 5 And Each One Being Perpendicular To Sum
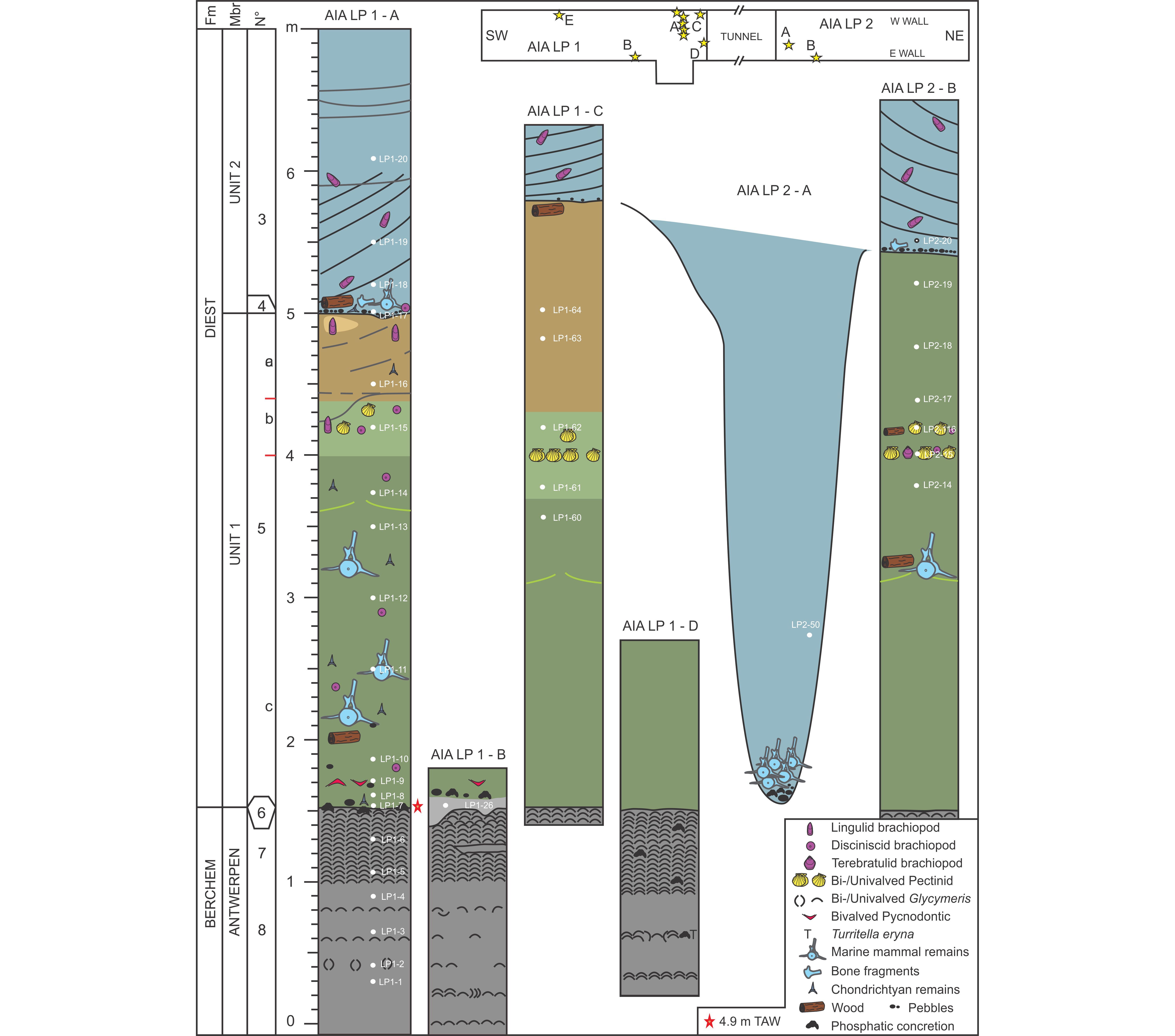



The Upper Miocene Deurne Member Of The Diest Formation Revisited Unexpected Results From The Study Of A Large Temporary Outcrop Near Antwerp International Airport Belgium Universite De Liege



Www Rtbf Be Auvio Detail Decibels La Quotidienne Id Http Ds Static Rtbf Be Image Media Object Default 16x9 19x1080 6 C 9 6c9c1e6d5399bbc7dc13c18c35 Jpg Decibels La Quotidienne Decibels Se Decline Aussi En Quotidienne
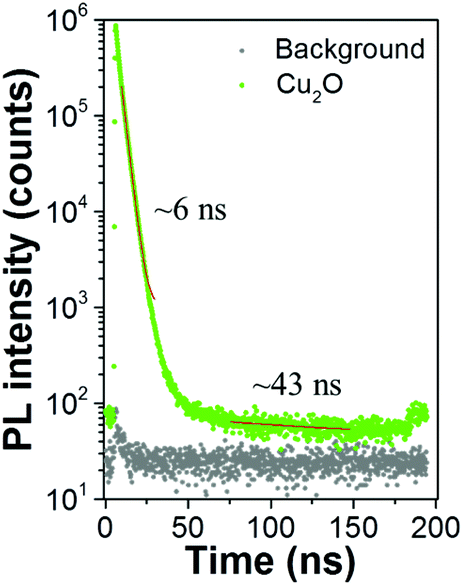



Oxygen Deficient Photostable Cu2o For Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity Nanoscale Rsc Publishing




A Room Temperature Xrd Patterns Of La 1ax Sr X Cu 0 925 Mn 0 075 So Download Scientific Diagram
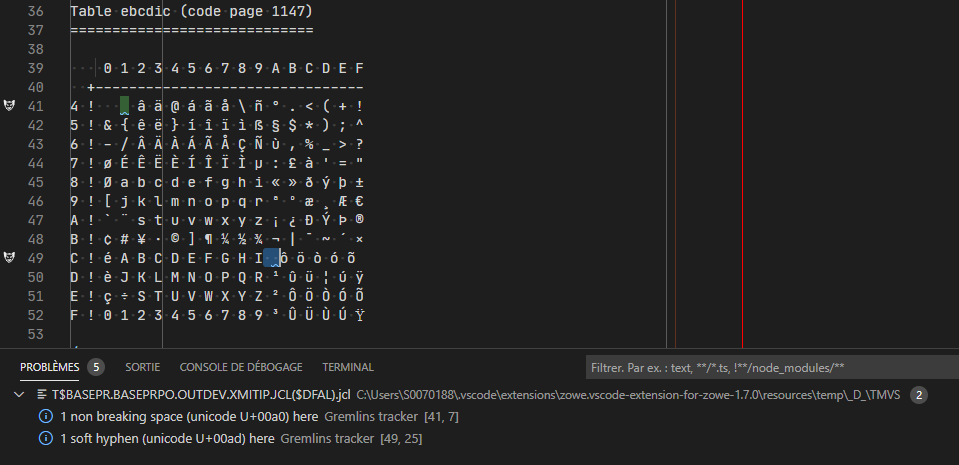



The Ebcdic X Ca Character Ibm 1147 Is Missing After Transfer With Zowe Explorer With Encoding 1147 Soft Hyphen X Ad Not Rendered By Chromium Issue 923 Zowe Vscode Extension For Zowe Github




5fa High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Bunaºs Hea Lua Ochta Na La Science 74 T Vini3s Tm Neoltjlocca A Aºit Os An A Ocf J Uf Indf Em M Ein T3lonn Un T Gt S Oife O Iix Pai Ein Ann Un U P A Oa Onn O Ocf Aijein Ut A Mjein P N A Oiiil J P
コメント
コメントを投稿